ADA-compliant Cabinet Heights For Wheelchair Accessibility
This comprehensive guide covers regulations, design considerations, and best practices for accessible kitchen and bathroom cabinets.
Keywords: ADA compliant cabinets, wheelchair accessible cabinets, accessible kitchen cabinets, accessible bathroom cabinets, ADA cabinet height requirements, wheelchair kitchen design, universal design, accessible bathroom design, kitchen accessibility, bathroom accessibility, disability accessibility, ADA standards, cabinet accessibility, accessible storage, ADA compliance, handicap accessible cabinets, low profile cabinets, adjustable cabinets, roll-under cabinets, accessible design principles
Introduction:
Designing spaces that are truly accessible for individuals with disabilities is paramount. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets standards to ensure equal access to public and commercial facilities, including crucial aspects like cabinet placement and height. For wheelchair users, accessible cabinet heights are not merely a convenience; they are essential for independent living and participation in daily tasks. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ADA-compliant cabinet heights, providing architects, designers, contractors, and homeowners with the knowledge needed to create inclusive and functional spaces.
Table of Content
Understanding ADA Standards and Cabinet Accessibility:
The ADA doesn’t explicitly state a single, universally applicable cabinet height. Instead, it focuses on providing a clear and unobstructed path of travel and reachable work surfaces. The key is to consider the reach range of a seated wheelchair user, which is significantly lower than that of a standing person. While there’s no specific "ADA cabinet height," the principles of accessibility dictate that cabinets must be positioned and designed to be readily accessible to individuals using wheelchairs.
Factors Influencing ADA-Compliant Cabinet Height:
Related Article ADA-compliant cabinet heights for wheelchair accessibility
- Wall-mounted Tool Cabinets For Organized Workshops
- Brown Gray Kitchen Cabinets: A Perfect Blend of Warmth and Elegance
- Kitchen Cabinets to Ceiling No Crown
- Black Cabinets with Gold Hardware: The Perfect Combination for a Modern Kitchen
- oak cabinets with granite countertops
Several factors interact to determine appropriate cabinet heights for wheelchair users:
- Seat Height of Wheelchair: The average wheelchair seat height ranges from 17.5 to 19.5 inches. Cabinet design must consider this variability to ensure accessibility for users with different wheelchairs.
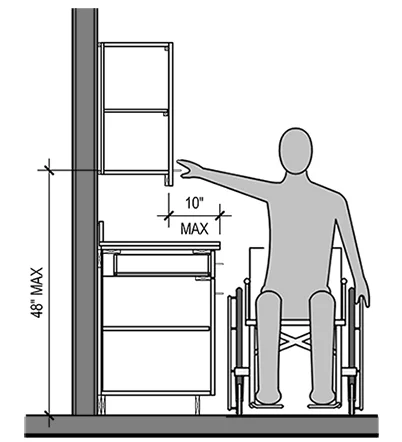
- Reach Range: A seated person’s reach is limited, both vertically and horizontally. The typical reachable range for a seated wheelchair user is approximately 48 inches from the floor, though this can vary depending on the individual’s upper body strength and flexibility. This range encompasses both forward and side reach.
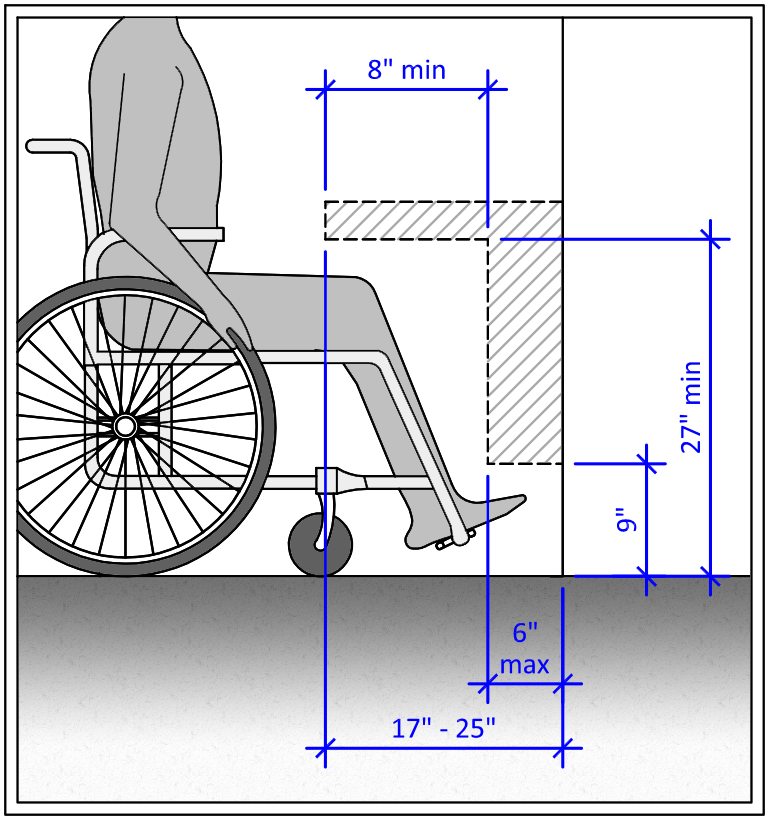
- Knee Clearance: Adequate knee clearance under cabinets is crucial for wheelchair maneuvering. The ADA recommends a minimum knee clearance of 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep.
- Cabinet Depth: While depth doesn’t directly affect height, it influences overall accessibility. Shorter, shallower cabinets can be easier to reach and access than deep ones.
- Cabinet Type: Different cabinet types (base cabinets, wall cabinets, tall cabinets) require distinct design considerations for accessibility.
Recommended Cabinet Heights for Wheelchair Accessibility:
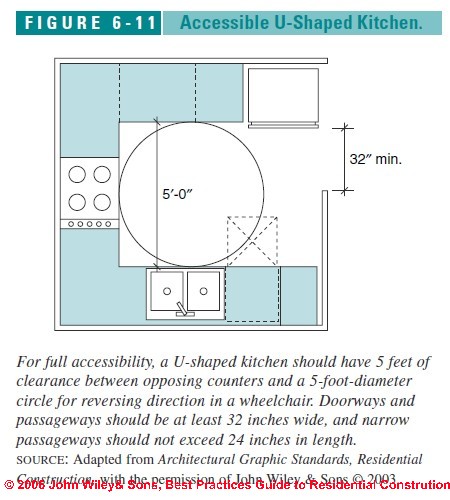
While there’s no mandated height, best practices suggest the following guidelines for ADA-compliant cabinet heights:
- Base Cabinets: Base cabinets should have a maximum height of 34 inches from the floor. This allows for comfortable reach for most seated wheelchair users. Ideally, consider a range of 28-30 inches for optimal accessibility. Lowering the countertop to 30 inches can further enhance usability.
- Wall Cabinets: Wall cabinets pose a greater challenge. While they can be positioned higher, they must be accessible. Consider lowering the bottom of the wall cabinets to a maximum height of 48 inches from the floor. This allows for comfortable reach for many users. However, this may necessitate adjustments to the overall kitchen design. Pull-down or lift-assist mechanisms can be incorporated for higher cabinets.
- Roll-Under Cabinets: These cabinets are designed with a recessed base, allowing wheelchairs to slide directly underneath. This eliminates the need to reach over or around obstacles. Roll-under cabinets are an excellent solution for maximizing accessibility. The countertop height remains the same as other base cabinets (28-30 inches).
- Adjustable Height Cabinets: Adjustable height cabinets offer a level of customization that caters to individual needs and preferences. This is an expensive solution but provides the highest degree of accessibility.
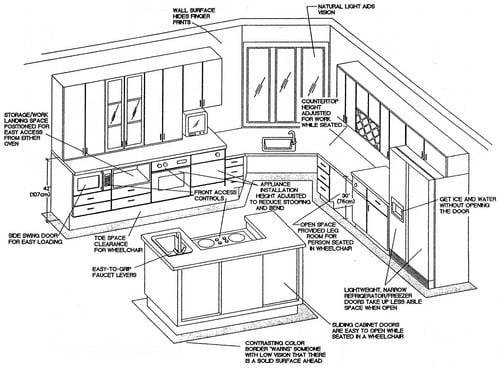
Designing for Universal Design Principles:
Designing for universal design means creating spaces accessible to people of all abilities. Incorporating universal design principles in cabinet design enhances usability for everyone, not just wheelchair users. These principles include:

- Clearance: Ensure ample clearance around cabinets for easy maneuvering.
- Grab Bars: Strategically placed grab bars can provide additional support and stability, especially in bathrooms.
- Easy-to-Use Hardware: Lever-style handles and knobs are easier to grip and operate than traditional round knobs.
- Accessible Storage: Organize frequently used items within easy reach.
- Lighting: Adequate lighting improves visibility and accessibility.
Specific Considerations for Kitchen and Bathroom Cabinets:
- Kitchen Cabinets: In kitchens, accessible cabinet placement is crucial for food preparation and storage. Consider placing frequently used items in lower cabinets within easy reach. Utilize pull-out shelves and drawers for improved access to items stored deeper within cabinets.
- Bathroom Cabinets: Bathroom cabinets should be positioned for easy access to toiletries and medications. Consider placing them at a height that allows for comfortable reach while seated. Roll-under sinks and vanities are highly recommended.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
While the ADA doesn’t specify precise cabinet heights, failure to provide reasonable access to cabinets can lead to legal challenges. It’s crucial to understand and apply the principles of the ADA and relevant accessibility guidelines to avoid non-compliance. Consulting with accessibility experts and reviewing local building codes is advisable.
Beyond ADA Compliance: Enhancing Accessibility and User Experience:
Going beyond minimum ADA requirements can significantly enhance the user experience. Consider these additional improvements:
- Ergonomic Design: Design cabinets with ergonomic principles in mind. This includes considering the user’s posture and movement patterns.
- Material Selection: Choose durable and easy-to-clean materials for cabinets.
- Color Contrast: Use contrasting colors to improve visibility of cabinet handles and knobs.
- Smart Technology Integration: Consider incorporating smart technology to automate cabinet opening and closing.
Conclusion:
Creating ADA-compliant cabinet heights requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. While there’s no single magic number, adhering to the principles of accessibility, universal design, and best practices ensures that cabinets are usable for individuals with disabilities. Prioritizing accessibility is not just about meeting legal requirements; it’s about fostering inclusion and empowering individuals to live independently and participate fully in their daily lives. By understanding the nuances of ADA compliance and incorporating innovative design solutions, we can create spaces that are truly accessible and welcoming for everyone. Remember to consult with professionals experienced in accessible design to ensure your project meets all relevant standards and regulations. Investing in accessible design is an investment in inclusivity and a better quality of life for all.