Ventilation Systems For Garage Welding Setups

Learn about different types, installation, maintenance, and best practices for optimal air quality.
Keywords: garage welding ventilation, welding fume extractor, welding ventilation system, garage welding safety, air filtration for welding, welding respirator, local exhaust ventilation, general ventilation, welding safety regulations, DIY welding ventilation, best welding ventilation system, cost of welding ventilation, welding smoke extractor
Welding is a rewarding skill, offering the ability to create and repair metal structures. However, the process generates harmful fumes and particulate matter that can seriously impact your health if not properly managed. A well-designed ventilation system is paramount for any garage welding setup, regardless of scale or frequency of use. This comprehensive guide will delve into the crucial aspects of garage welding ventilation, helping you create a safe and productive workspace.
Understanding the Dangers of Welding Fumes
Table of Content
Welding fumes contain a complex mixture of substances, varying depending on the metal being welded and the filler material used. These can include:
- Metal oxides: These are formed when the metal heats up and reacts with oxygen in the air. Examples include iron oxide (rust), chromium oxide, manganese oxide, and nickel oxide. Many are carcinogenic or linked to respiratory illnesses.
- mediterranean style garage doors
- The Beauty and Durability of Mahogany Garage Doors
- rv roof cover ideas
- level garage door
- Garage Spring Danger: Understanding the Risks Involved
- Ozone: Welding arcs produce ozone, a highly reactive gas that can irritate the lungs and eyes.
- Nitrogen oxides: These gases are formed when the high temperatures of welding break down nitrogen in the air. They can cause respiratory problems.
- Fluoride compounds: These are released when welding certain metals or using specific filler materials. They can cause respiratory irritation and dental fluorosis.
- Particulate matter: Tiny particles of metal and other materials are released during welding. These can be inhaled deep into the lungs, causing serious health problems.
Related Article Ventilation systems for garage welding setups

The long-term effects of exposure to these fumes can be devastating, including:
- Metal fume fever: A flu-like illness caused by exposure to metal fumes.
- Respiratory diseases: Including bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer.
- Cardiovascular problems: Some studies link welding fume exposure to an increased risk of heart disease.
- Neurological disorders: Certain metals in welding fumes can affect the nervous system.
- Cancer: Several components of welding fumes are classified as carcinogens.

Types of Welding Ventilation Systems

Effective ventilation requires a multi-pronged approach, often combining different methods. The primary types include:
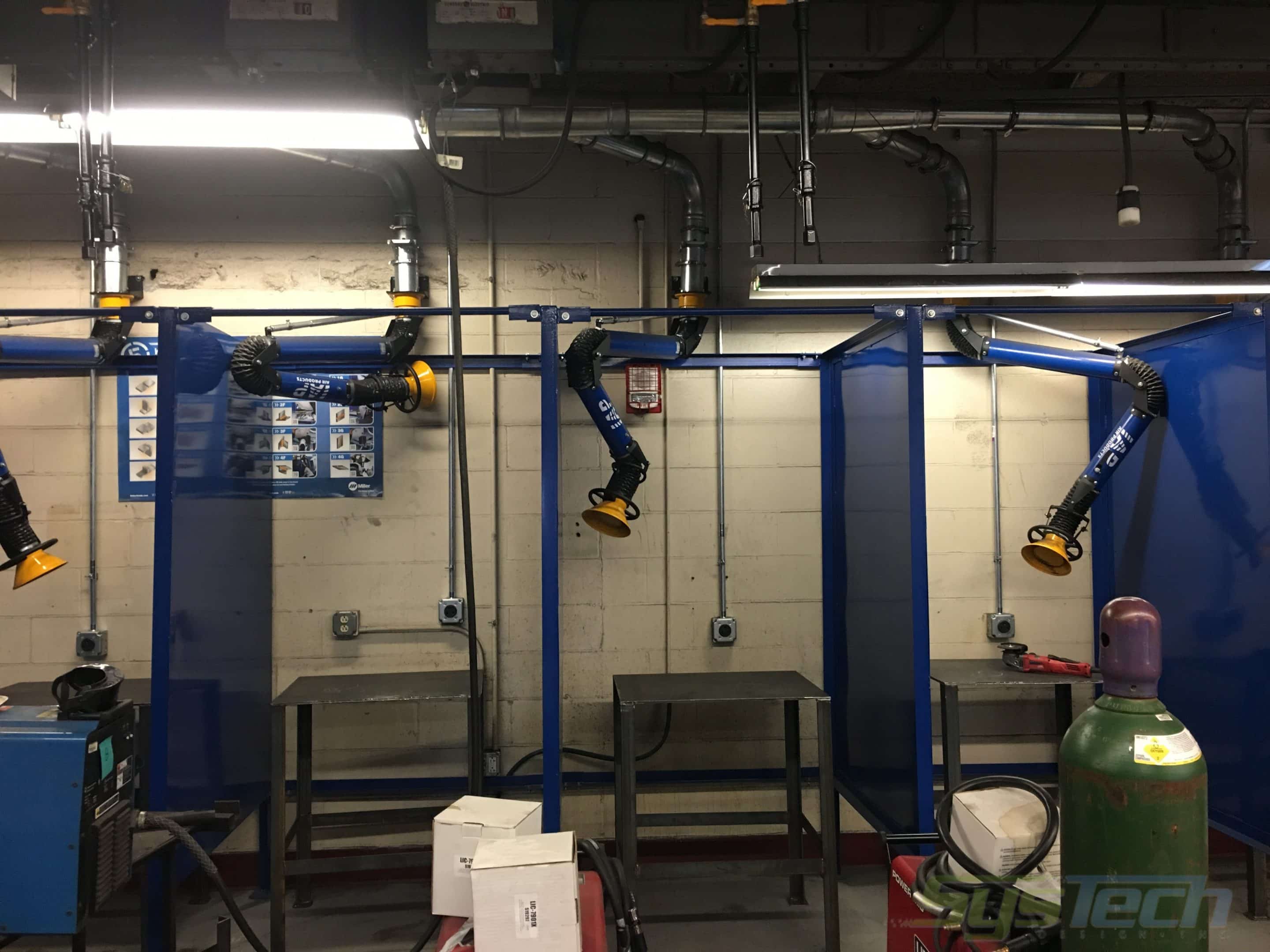
1. Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV): This is the most effective method for controlling welding fumes at their source. LEV systems use a hood or nozzle placed close to the welding arc to capture fumes before they disperse into the air. The fumes are then drawn through a ductwork system to a filter or outside the building.
- Advantages: Highly effective at removing fumes, minimizes overall air movement, reduces energy consumption compared to general ventilation.
- Disadvantages: Can be expensive to install, requires careful design and placement of the hood to be effective, may require professional installation. Different hoods are needed for different welding processes (e.g., MIG, TIG, stick).
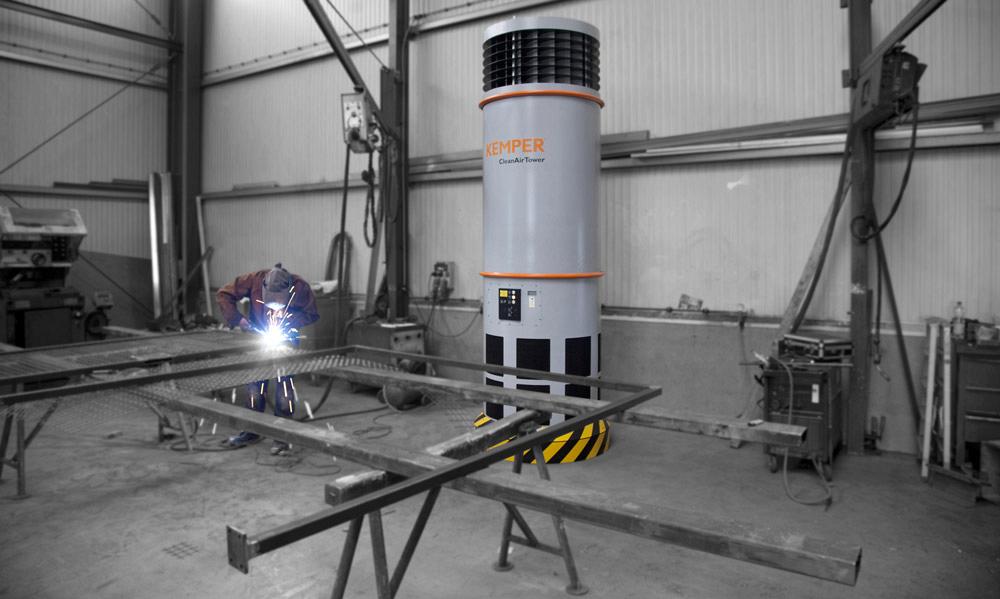

2. General Ventilation: This involves using fans or other methods to create airflow throughout the garage, diluting the concentration of welding fumes. It’s often used in conjunction with LEV systems.
- Advantages: Relatively inexpensive and easy to install. Improves overall air quality in the garage.
- Disadvantages: Less effective at removing fumes than LEV, requires significant airflow to be effective, can be energy-intensive.
3. Air Filtration Systems: These systems use filters to remove particulate matter and other pollutants from the air. They can be used as a standalone system or in conjunction with LEV and general ventilation. HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are particularly effective at removing small particles.
- Advantages: Removes particulate matter from the air, can be effective at removing odors, relatively easy to install.
- Disadvantages: May not be effective at removing all types of welding fumes, filters need regular replacement, can be expensive depending on the size and filter type.
Choosing the Right Ventilation System for Your Garage
The best ventilation system for your garage will depend on several factors:
- Frequency of welding: Occasional welders may only need general ventilation, while frequent welders will require a more robust system, possibly incorporating LEV.
- Type of welding: Different welding processes generate different types and amounts of fumes. MIG welding, for example, often produces more fumes than TIG welding.
- Size of the garage: Larger garages will require more powerful ventilation systems.
- Budget: Ventilation systems can range in cost from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars.
- Local regulations: Check your local regulations for any requirements regarding welding ventilation.
Installation and Maintenance of Welding Ventilation Systems
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for the effectiveness and longevity of your ventilation system.
LEV Installation: Professional installation is often recommended for LEV systems to ensure proper hood placement, ductwork design, and fan selection. Improper installation can lead to reduced effectiveness or even safety hazards.
General Ventilation Installation: Installing general ventilation systems can be a DIY project, but it’s important to ensure adequate airflow and proper fan placement. Consider using multiple fans strategically placed to maximize airflow.
Air Filtration System Installation: Air filtration systems are relatively easy to install, but choosing the right filter type and size is important. Make sure the system has sufficient capacity for your garage size and welding activity.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for all ventilation systems. This includes:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean dust and debris from filters, ducts, and fans.
- Filter replacement: Replace filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. For HEPA filters, this might be every 6-12 months, depending on usage.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the system for any damage or leaks.
- Fan maintenance: Ensure fans are running efficiently and lubricate as needed.
Additional Safety Precautions
Even with a robust ventilation system, other safety precautions are necessary:
- Respiratory protection: Always use a welding respirator or helmet with appropriate filters, even with ventilation in place. This provides an extra layer of protection.
- Eye protection: Wear appropriate eye protection to protect against sparks and UV radiation from the welding arc.
- Protective clothing: Wear fire-resistant clothing to protect against sparks and hot metal.
- Proper ventilation: Ensure adequate fresh air supply to the garage to prevent oxygen depletion.
DIY Welding Ventilation: A Word of Caution
While some aspects of ventilation system installation can be DIY, attempting complex LEV systems without proper knowledge and experience is strongly discouraged. Improper installation can lead to ineffective fume removal, creating a false sense of security. Always prioritize safety and consult with professionals if unsure.
Cost Considerations:
The cost of a welding ventilation system can vary greatly depending on the type and complexity of the system. Simple general ventilation solutions can be relatively inexpensive, while sophisticated LEV systems with advanced filtration can cost several thousand dollars. Factor in installation costs, ongoing maintenance expenses, and filter replacements when budgeting.
Conclusion:
Investing in a proper welding ventilation system is not merely a cost; it’s an investment in your health and safety. The long-term consequences of exposure to welding fumes can be severe, making effective ventilation a non-negotiable aspect of any garage welding setup. By understanding the different types of systems, their installation, and maintenance requirements, you can create a safe and productive welding environment for years to come. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult with professionals when needed. Your health is invaluable.